Lecture04 Rendering in Game Engine
挑战
- 场景极其复杂
- 实时,帧率稳定
大纲
- 基础
- 硬件架构
- 渲染数据结构
- 可见性
- 材质、Shader、光照
- PBR
- Shader Permutation
- 光照
- 点/方向光照
- IBL / Simple GI
- 特殊的渲染
- 地形
- 天空 / 雾
- 后处理
- Pipeline
- 前向渲染 Forward、延迟渲染 Deferred、Forward Plus
- Ring buffer and V-Sync
- Tiled-based Rendering
@GAMES101
Vertex Data -> Triangle Data -> Material Parameters -> Textures
投影 -> 光栅化
eg. Computation - Texture Sampling
- Step 1 : 使用相邻两层MIPMAP
- Step 2 : 在两层MIPMAP之间双线性插值
- Step 3 : 结果像素之间的线性插值
GPU
SIMD and SIMT
SIMD : Single Instruction Multiple Data eg.四维向量同时加减
SIMT : Single Instruction Multiple Threads 同时处理大量SIMD任务
计算单元
- GPC Graphics Processing Cluster
- SM Streaming Multiprocessor
- Texture Units
- CUDA Core
- Warp (a collection of threads)
Application Performance is limited by:
- Memory Bounds
- ALU Bounds
- TMU(Texture Mapping Unit) Bound
- BW(Bandwidth) Bound
Renderable - 可渲染的内容(Component)
- Mesh
- Mesh Primitives
- Vertex and Index Buffer > 每顶点存储法向:避免有两个顶点重合时法向错乱
- Material
- Textures
- Shaders
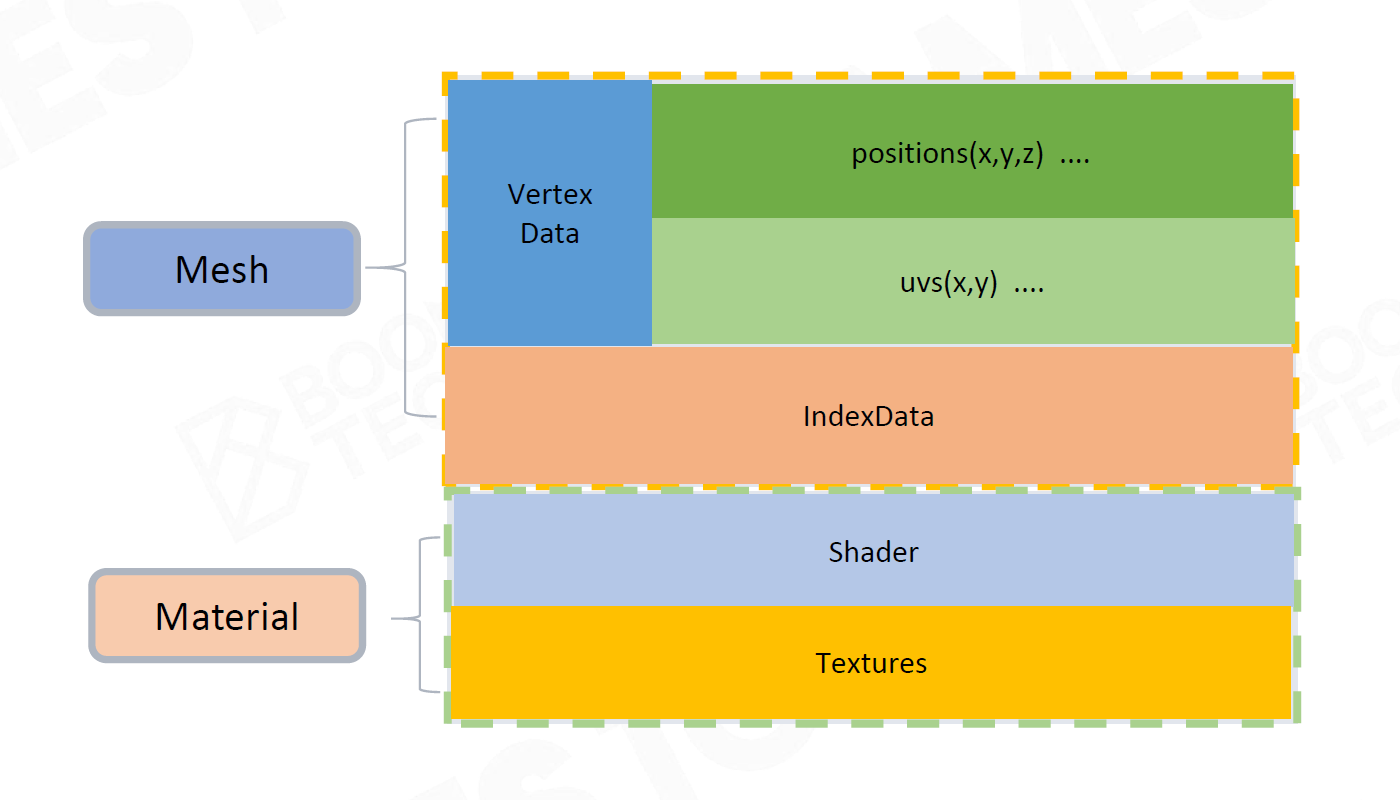
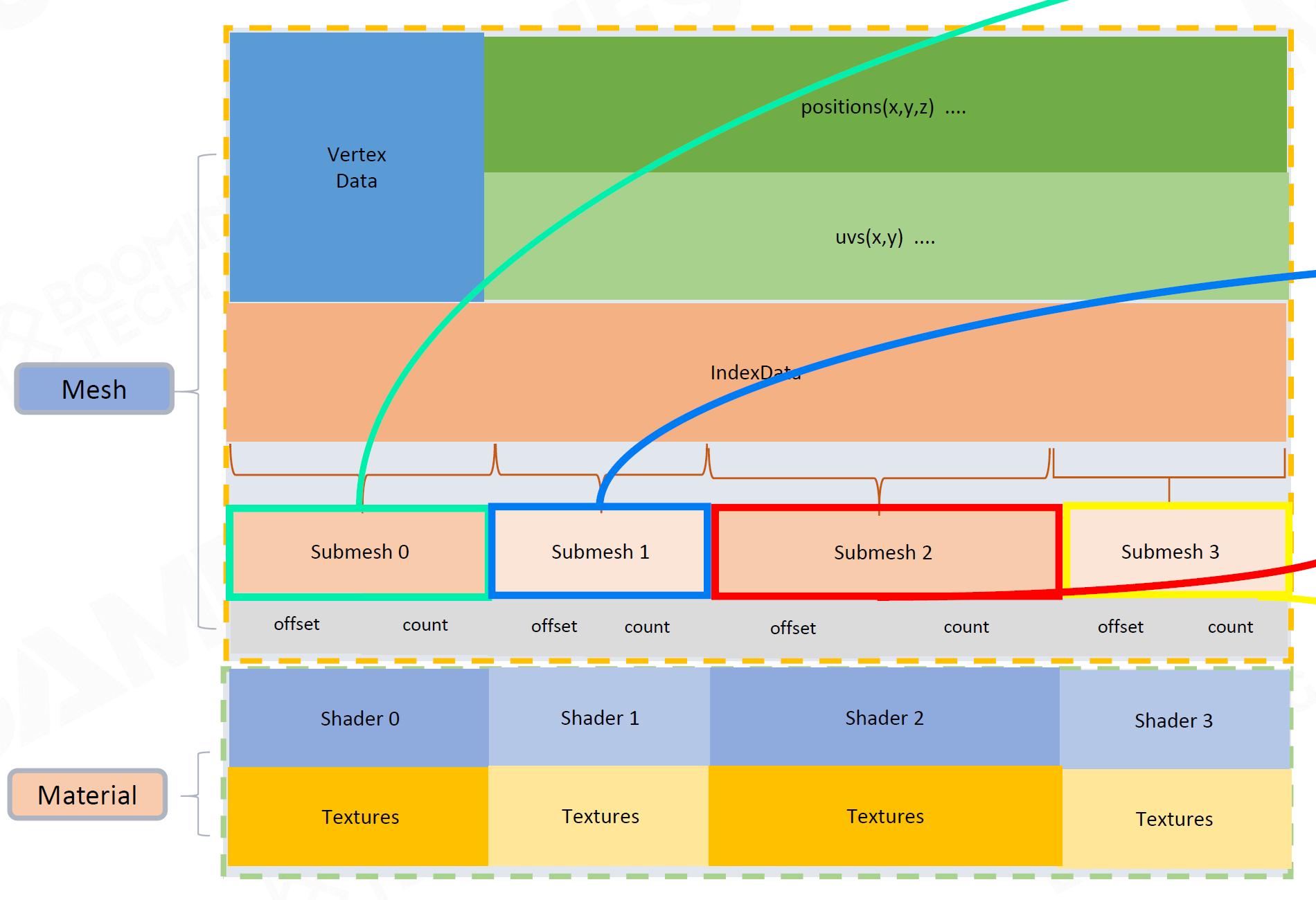
一个Mesh有多种材质 —— SubMesh
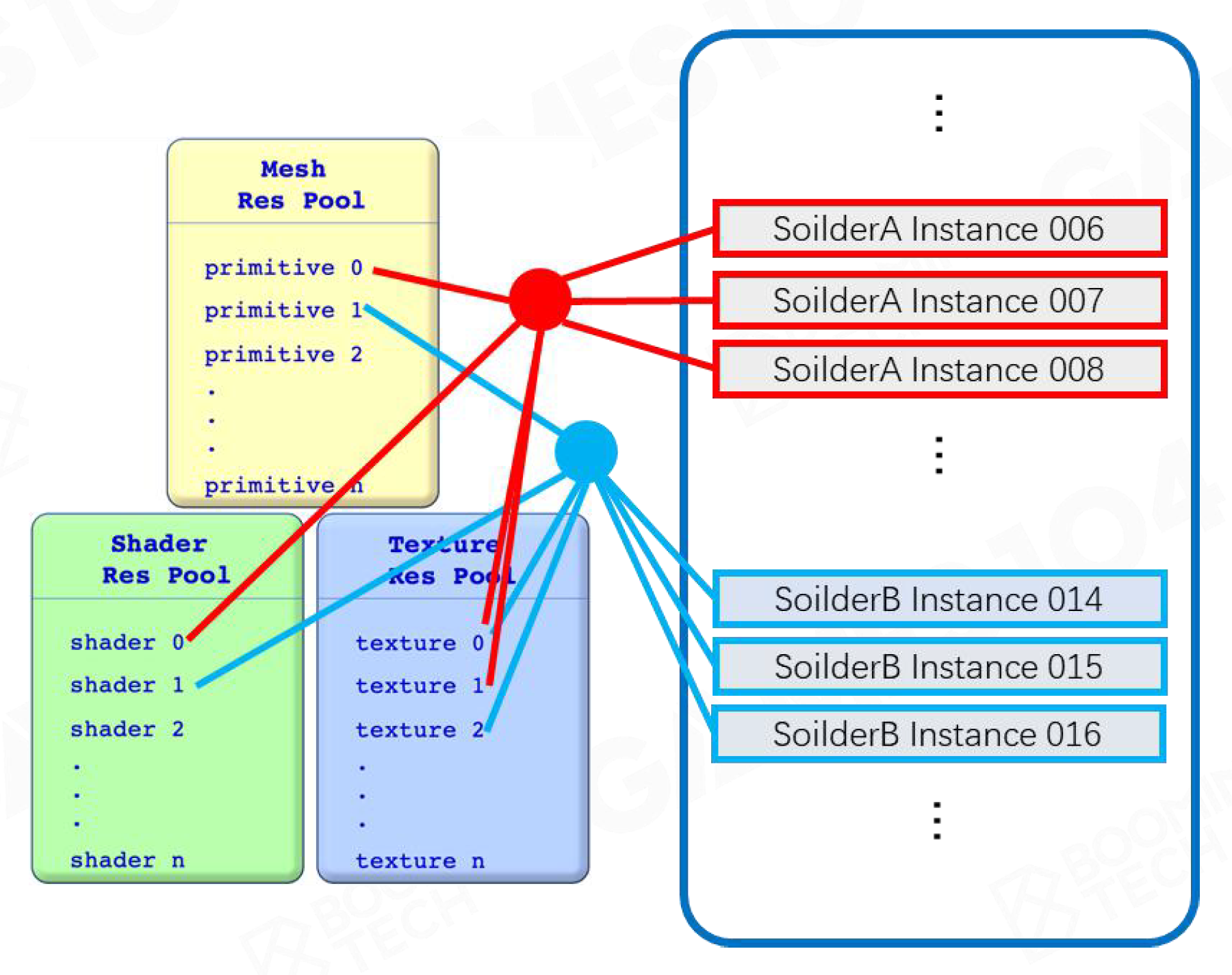
节约空间:Mesh / Shader / Texture 各存储一个Pool,使用时用索引 —— Instance
对场景按场景排序渲染 —— 对GPU友好,可以加速
GPU Batch Rendering 渲染一次,再做Offset
Visibility Culling
- View Frustum之外的不渲染
- 对空间做划分(前文介绍,四叉树 / BVH) BVH构建块,应用多
- PVS, Potential Visibility Set 根据房间门是否可见裁剪
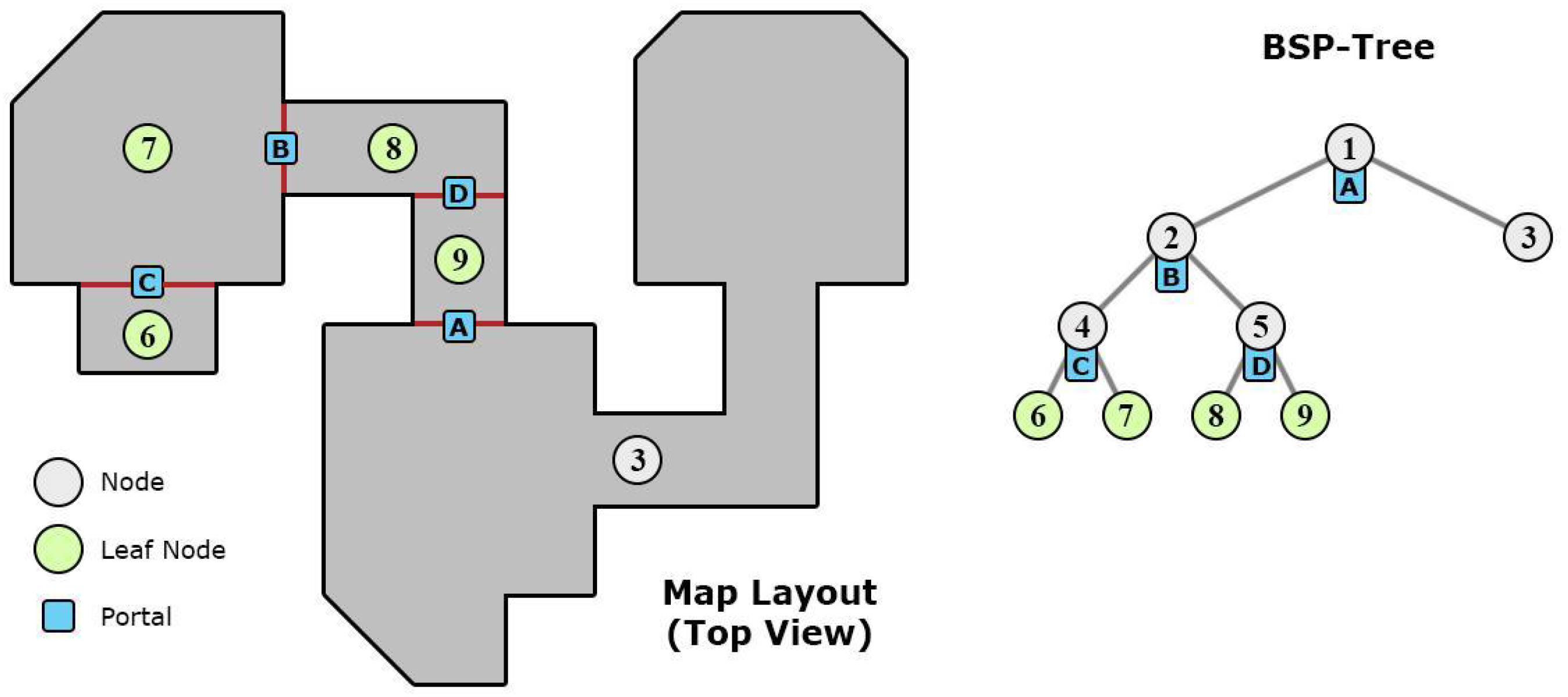 现在已应用不广,但思想可以用于资源加载等场景
现在已应用不广,但思想可以用于资源加载等场景 - GPU Culling 利用G-Buffer,延迟渲染
纹理压缩
- 不能用JPG/PNG等复杂压缩
- Block Compression:将图片切分为一个个小块(例如4*4)压缩 eg. 在小块中保留最大值最小值,其他值使用这两值的线性插值
Authoring Tools of Modeling
- Polygon : MAX / MAYA / Blender
- Sculpting : Zbrush
- Scanning
- Procedural : Houdini
Cluster-Based Mesh Pipeline
- 核心思想:对于非常精细的模型,将其分成无数一组面片组成的Cluster
- 提供Mesh Shader:GPU处理同样的Cluster,实现更精细的细节
- 可以基于Cluster做裁剪
- Nanite in UE5